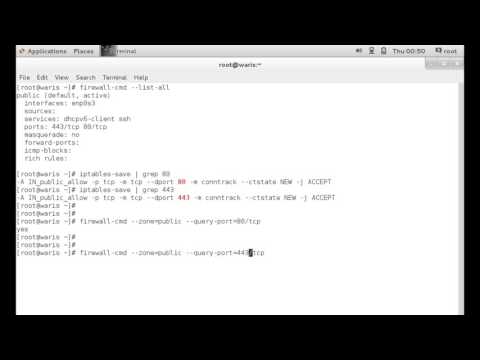
The netstat command shows the services listening to ports on a Linux server and the details of any connections currently made to them. The ss command in Linux provides significant information about network connections including open ports and listening sockets. It gets this information from the Linux kernel. The ss command is the substitute of netstat command. The ss command is bundled with the iproute2 package and available on the Debian system.
However, in any case, if you do not find it in your system, you can install it easily. There are two basic approaches for listing the ports that are listening on the network. The less reliable approach is to query the network stack by typing commands such as netstat -an or lsof -i. This method is less reliable since these programs do not connect to the machine from the network, but rather check to see what is running on the system. For this reason, these applications are frequent targets for replacement by attackers.
In this way, crackers attempt to cover their tracks if they open unauthorized network ports. Ss command is another useful tool for displaying information about sockets. It's output looks similar to that of netstat. The following command will show all listening ports for TCP and UDP connections in numeric value.
The netcat tool can be described as a command-line utility to read and write data across many network connections on the UDP and TCP protocols. This tool can implement tests over a particular port or a variety of ports. If you want to know the program's name that has a specific port open, then type netstat -aon and press Enter.
This command will show the protocol the app is using, the local and remote IP addresses, and most importantly, the PID of the application using that port . If you make any changes because the incorrect service is listening, run the netstat command again. If netstat doesn't show the program listening on the correct port, you need to address its configuration before you go any further. Some network tools and utilities can simulate an attempt to establish a connection to a specific port and wait to see if the target host responds. If there is a response, the target port is open.
If not, the target port is closed, or the host is unable to accept a connection because there is no service configured to listen for connections on that port. The ping command is a network tool for checking whether a remote system is up and running. In other words, the command determines if a certain IP address or a host are accessible. Ping uses a network layer protocol called Internet Control Message Protocol and is available on all operating systems. When troubleshooting your network connection, it is important to test all of the addresses and ports used by your Code42 app to connect to the Code42 server.
The examples later in this article use addressclients.us.code42.com; in addition to this address, make sure to test all of the addresses that the Code42 app uses. A failed connection will be accompanied by an error message. It can indicate either a closed port or the fact that the indicated remote server is not listening on the provided port. A more reliable way to check which ports are listening on the network is to use a port scanner such as nmap. Many important applications like database servers, web servers, file transfer services, etc., use dedicated ports. Using pipe and grep commands, the result of the above command can be filtered to show the result of files that are listening on different ports in the server.
I have some servers and I want to check which ports are open. Open ports give clue about the load and security about the system. Open ports mean there is services running on the server and clients are using these so a load of this system is generally higher than other servers.
Also, open ports will prevent services to use the same port as Nginx and Apache. Checking for ports is very important to verify which ports are opened and listening on your system. Listening services can be an entry point for hackers who can exploit vulnerabilities in systems to gain access or compromise a system. It is not recommended to keep a service running if you are not using it.
Therefore, it is necessary to keep a continuous check on open ports on your system. To find open ports on a computer, you can use netstat command line. To display all open ports, open DOS command, type netstat and press Enter. To list all listening ports, use netstat -an |find /i "listening" command. To find specified open port, use find switch.
To check if port is open, you should enter "netstat -a" in the command line and it will return with a list of open ports. Before opening a port on Linux, let us first check the list of all open ports, and choose an ephemeral port to open from that list. We can use the netstat command to list all open ports, including those of TCP, UDP, which are the most common protocols for packet transmission in the network layer.
In the command prompt window, type "telnet" followed by a space, then an IP address or domain name followed by another space, and then the port number. For example, to check whether you can connect to port 80 on , you type "telnet 80" in the command prompt window. Let's say we recognize a suspicious process within our system and we wish to check related ports to it. We can use the lsof command which is used for listing open files related to processes. Every example above displays how to print the details over listening ports without authorized connections. The below commands display how to show listening ports and authorized connections.
You'll see a long list of results, depending on what's currently connecting to the network. The open port numbers will be after the last colon on the local IP address . Vulnerable open ports can be the cause of severe security breaches in a server. It is a must that such ports are found out and closed/disabled. To see if a program or process is listening on a port, ready to accept a packet, use the netstat command. I don't know why lsof is slow for you, but normally it is the best of the solutions you listed.
Your netstat solution is not very reliable (you can guess it whenever you use grep; anyway it returns true if someone is listening on e.g. 4450). Telnet and netcat actually attempt to create a connection, which may not always be what you want. Nmap is one of the most popular and advanced network scanner tools. It is open-source and freely available for Unix and Windows systems. NmapFE is a graphical version of the terminal-based nmap command.
It has a vast feature set of operations like port scanning, protocol scanning, OS fingerprinting , etc. Apart from ss / netstat one can use the lsof command to list open files and ports on Linux based system. One of the widely used commands is to check if a remote host is responding to ICMP ECHO_REQUEST or not. Keep in mind, this may not give you accurate results when ICMP is blocked at the remote network's firewall. Assuming that's not the case, you can ping to IPv4 or IPv4 network endpoint as below.
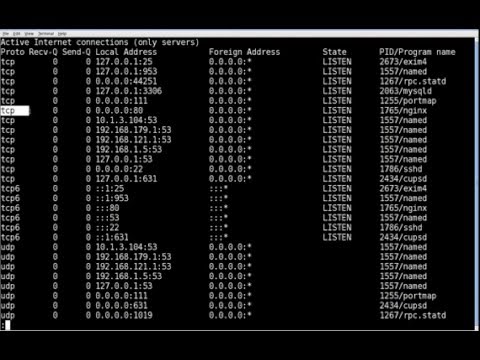
The netstat tool can be described as a utility to display network connections for routing tables, TCP, and several network interfaces. Also, it facilitates statistics of network protocol. We could list every open port of a system by using the netstat tool. Sometimes the Code42 app can't make a network connection even if the Internet appears to be working.
This is because the Code42 app relies on specific ports to be open. This article describes how to test connectivity on the correct ports to rule out problems with firewalls, anti-virus products, or other network issues. Step 2 — Using telnet command to check if port 587 is open. Now, once you have your terminal window open, write down the following line. You can first try to use ping to check if there is network connectivity.
Then do a telnet to the host name for a specific port. If the firewall to the specific host and port is enabled, then it will make a connection. Applications running on your computer reach out and get information and data from servers elsewhere on the internet. These applications and the server know how to communicate based on their IP address and the port number. Note that nmap will only list open ports that are listening for connections. That's why we use netcat for testing, to listen on that port.
Otherwise, the port won't register as being open. In Windows servers, the netstat command can be used to check the ports that are currently in use in the server. Nmap is a security tool which is used by pentesters and hackers. Nmap is very useful so we can use it to find open ports. Nmap can be used to find open ports on localhost or remote host even on the internet.
To get more information about nmap to look at our Nmap Tutorial. Netstat is another useful tool which provides network related information about the host. Following command will check both TCP and UDP ports which are in listen mode or open.
You can check Open ports in Linux using utilities like netstat, ss, lsof and nmap etc. On the latest version of Linux system the ss command is mainly used. For UDP ports, the system sends a UDP datagram with a ping to the back-end server port. If the back-end server responds with Internet Control Message Protocol port unreachable or ICMP unreachable, the back-end port is considered unreachable. You can enter an IP address, hostname or FQDN for the target server.
Both incoming and outgoing connections, routing tables, port listening, and usage statistics are common uses for this command. Many people find the challenge of checking if a port is opened to be too complex. However, one of the most efficient ways is to use the network protocol Telnet. Telnet allows the user to test individual ports and see whether they are open or not.
In this article we'll break down how Telnet can be used to check ports on Windows 10, Windows Server 2016, 2012 and 2008. When it comes to checking if a network port is opened or closed on a remote computer, there's no easier way than to use Telnet. Ports that are left open for no reason are a security risk that can be exploited by malicious programs and viruses.
At the same time, if a legitimate software communicates through a certain port, having that port closed will make the program throw errors and malfunction. The final tool we will cover for querying open ports is lsof command, which is used to list open files in Linux. Since everything is a file in Unix/Linux, an open file may be a stream or a network file. In this article, we will explain four ways to check open ports and also will show you how to find which application is listening on what port in Linux. The state of a port is either open, filtered, closed, or unfiltered.
A port is said to be open if an application on the target machine is listening for connections/packets on that port. To determine if someone is listening, attempt to connect by loopback. If it fails, then the port is closed or we aren't allowed access. TELNET is a client/server application for remote login to a server with virtual terminal capability across a network.
It uses TCP's port number 23 over a TCP/IP network. RFC 854 defines the specification for the TELNET protocol. Another option is to use the netstat command to list all ports in Linux. The last command that we are going to discuss is the netstat command. It is used to print connections, interface statistics, multicast membership, and other network-related tasks.
To do so, it utilizes a novel approach to using IP packets. It can also be used to learn about the services the host is providing. Other vital aspects that it can detect include operating system version, packet firewalls/filters, and so on!
That will test if that there's a web server configured for SSL. Note that this test using telnet is only going to work if the process is listening on a TCP port. If it's a UDP port, you may as well try with whatever client you were going to use to connect to it. (I see that you used port 224. This is masqdialer, and I have no idea what that is).
There are so many ways for checking open ports in Linux. By default, a port will close unless any application is applying it. A port should be assigned to a process or service if it is open.
If the connection test passes, there probably isn't an issue with the network. However, some firewall and anti-virus applications are capable of blocking connections on a per-application basis. Make sure the Code42 app has an exception configured in your security software. If the problem continues, contact your administrator. This option represents the internet connection firewall. On the server itself, use netstat -an to check to see which ports are listening.